IMAGE OF THE MONTH: May 2022
Retinal Blebs
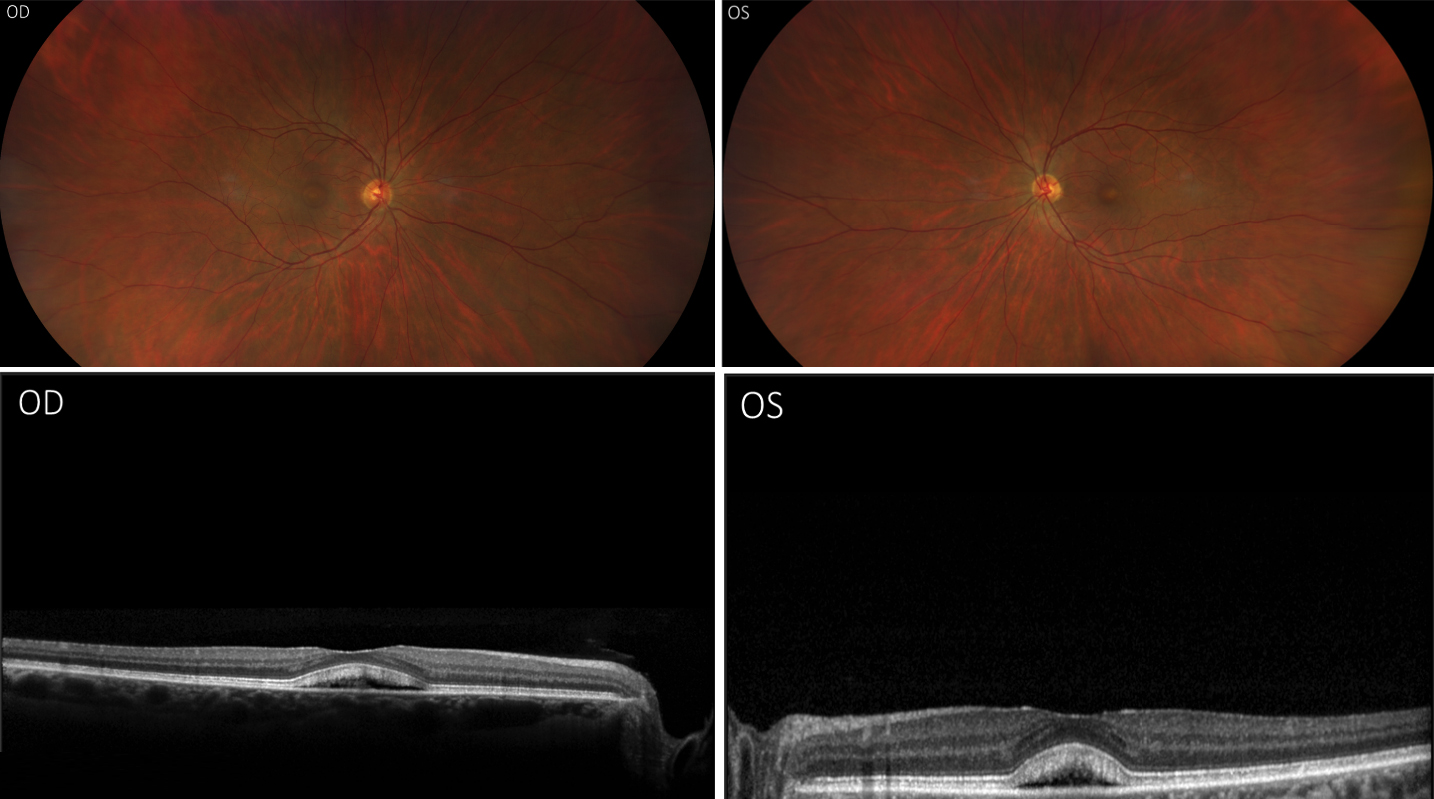
55 year old Caucasian female with a history of bladder cancer was referred for retinal abnormalities. VA 20/25 and 20/30
DIAGNOSIS
Differential Diagnosis
- Central serous chorioretinopathy
- Medication toxicity
Definitive Diagnosis
- Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) Inhibitor–Associated Retinopathy (aka FGFR inhibitor associated pseudocentral chorioretinopathy)
Discussion:
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Antagonists
- Epidemiology: Few studies on FGFR antagonist associated retinopathy. Francis et al. reported 20 of 146 patients who developed retinopathy as a consequence of FGFR antagonist medication in a case study published in October 2021 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
- Presentation: asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic subretinal fluid.
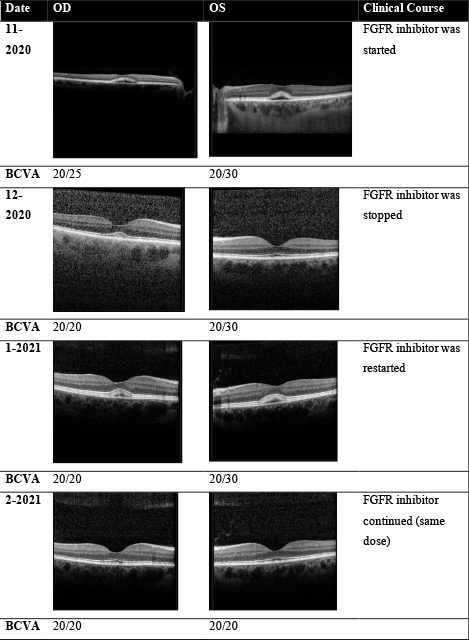
- Clinical Course: self-resolving without medication discontinuation (Francis et al.). However, only few studies have described the condition, and all were retrospective.
- Management: No RCTs to guide best therapeutic strategy but liaising with the oncologist is the best current option.
- Side Notes: The retinopathy seen with FGFR inhibitors is very similar to that shown with MEK and ERK inhibitors.
- Both have bilateral serous elevations that often surround the fovea.
- Fluid accumulates between the retinal pigment epithelium and the interdigitation zone on OCT.